Everything You Need To Know About Injection Molding
What is Injection Molding?
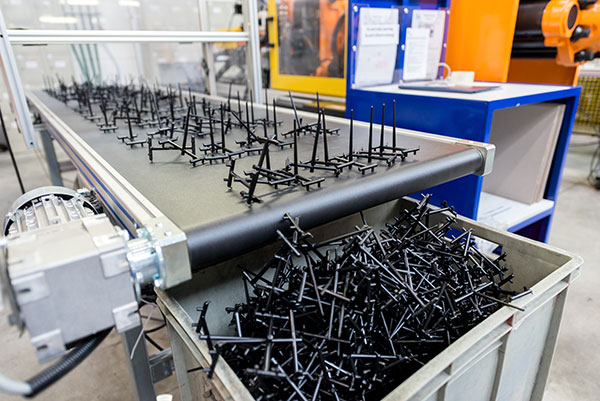
Injection Molding is a manufacturing process for producing parts in large volume. It is most typically used in mass-production processes where the same part is being created thousands or even millions of times in succession.
What polymers are used in injection Moulding?
The table below lists some of the commonly used materials:
Acrylonitrile-Butadiene-Styrene ABS.
Nylon PA.
Polycarbonate PC.
Polypropylene PP.
Polystyrene GPPS.
What is the process of injection molding?
The plastic injection moulding process produces large numbers of parts of high quality with great accuracy, very quickly. Plastic material in the form of granules is melted until soft enough to be injected under pressure to fill a mould. The result is that the shape is exactly copied.
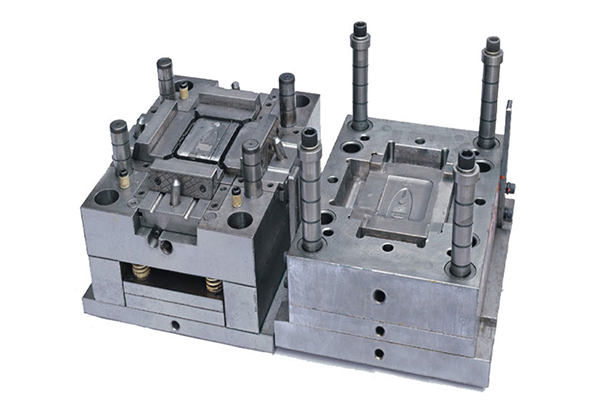
What is the injection molding machine?
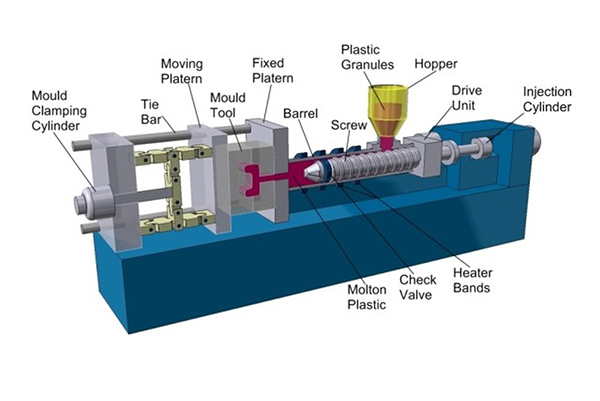
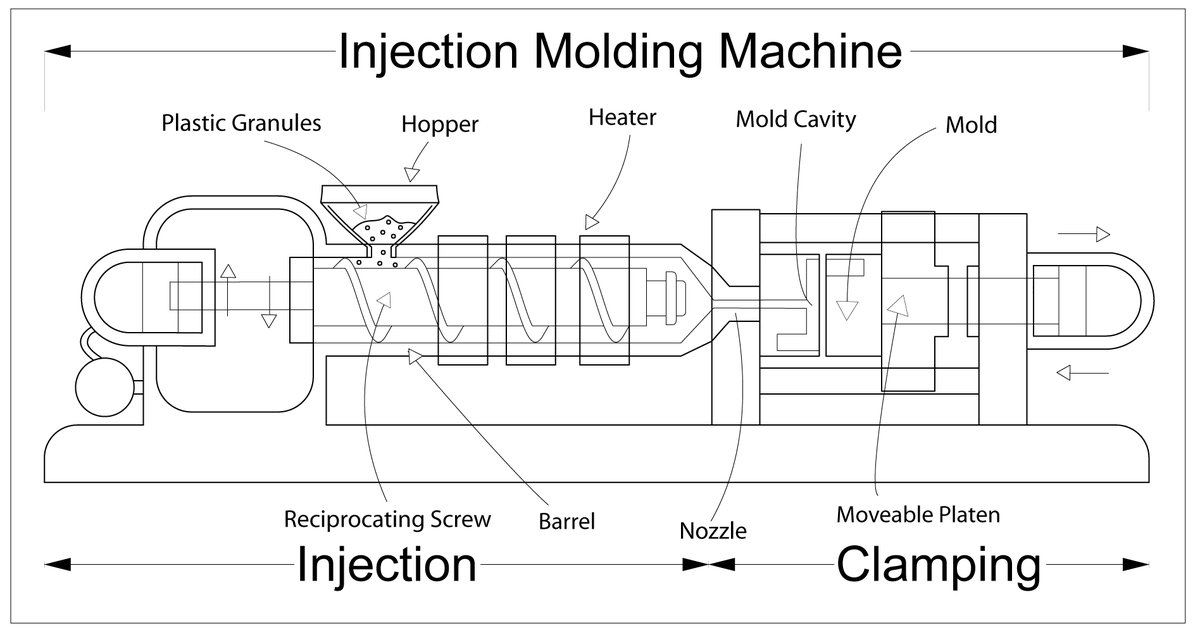
An Injection molding machine, or (Injection moulding machine BrE), also known as an injection press, is a machine for manufacturing plastic products by theinjection molding process. It consists of two main parts, an injection unit and a clamping unit.
How do injection molding machines work?
Material granules for the part is fed via a hopper into a heated barrel, melted using heater bands and the frictional action of a reciprocating screw barrel. The plastic is then injection through a nozzle into a mould cavity where it cools and hardens to the configuration of the cavity.
What Are Some of The Considerations For Injection Molding?
Before you endeavor to produce a part via injection molding consider a few of the following things:
1, Financial Considerations
Entry Cost: Preparing a product for injection molded manufacturing requires a large initial investment. Make sure you understand this crucial point up front.
2, Production Quantity
Determine the number of parts produced at which injection molding becomes the most cost effective method of manufacturing
Determine the number of parts produced at which you expect to break even on your investment (consider the costs of design, testing, production, assembly, marketing, and distribution as well as the expected price point for sales). Build in a conservative margin.
3, Design Considerations
Part Design: You want to design the part from day one with injection molding in mind. Simplifying geometry and minimizing the number of parts early on will pay dividends down the road.
Tool Design: Make sure to design the mold tool to prevent defects during production. For a list of 10 common injection molding defects and how to fix or prevent them read here. Consider gate locations and run simulations using moldflow software like Solidworks Plastics.
4, Production Considerations
Cycle Time: Minimize cycle time in as much as it is possible. Using machines with hot runner technology will help as will well-thought-out tooling. Small changes can make a big difference and cutting a few seconds from your cycle time can translate into big savings when you’re producing millions of parts.
Assembly: Design your part to minimize assembly. Much of the reason injection molding is done in southeast Asia is the cost of assembling simple parts during an injection molding run.
Post time: Nov-05-2020